600
83
80
76
SyncFrame: A Unified Approach for Harmonizing ESG Reporting and Driving Global Collaboration
The field of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting has witnessed a proliferation of frameworks and standards, each with distinct methodologies and priorities. This diversity, while valuable in addressing specific contexts, poses a challenge for organizations aiming to effectively communicate their sustainability performance and for stakeholders seeking comparability across diverse entities.
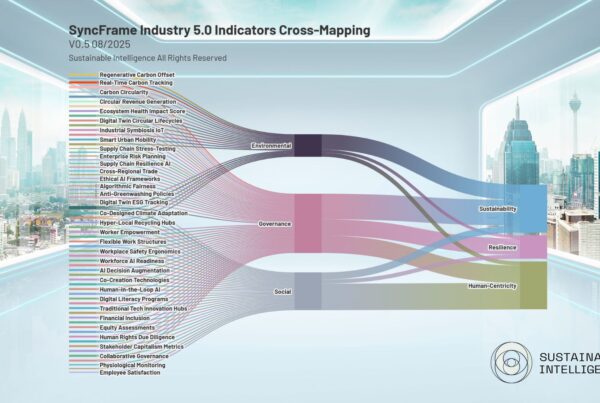
SyncFrame addresses this fragmentation by offering a universal framework that aligns with and translates a multitude of existing standards. This interoperability not only streamlines reporting processes but also fosters global collaboration and facilitates informed decision-making.
”By 2020 there were over 600 sustainability reporting instruments in 87 countries worldwide.
Carrots & Sticks2020 Report
A Comprehensive Approach to Alignment
SyncFrame’s interoperability is a testament to its comprehensive design and commitment to inclusivity. The framework harmonizes with a broad spectrum of established standards, including:
- Globally Recognized Frameworks: Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards, Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) Standards, Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) Recommendations, UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) Framework.
- International Standards: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System), ISO 26000 (Guidance on Social Responsibility).
- Emerging Standards: European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD).
- Industry-Specific Standards: Sustainability Initiative of South Africa (SIZA), Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct, Equator Principles, Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC) Code of Practices, Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) Criteria, Sustainable Apparel Coalition (SAC) Higg Index.
This broad alignment enables organizations to leverage their existing ESG reporting efforts while benefiting from a standardized approach that enhances comparability and reduces the administrative burden.
Facilitating Global Collaboration
By providing a common language for sustainability, SyncFrame facilitates collaboration and information sharing across borders, industries, and sectors. This harmonization of ESG reporting enables stakeholders to:
- Compare Performance: Investors can more easily assess the ESG performance of different companies, facilitating informed investment decisions.
- Identify Best Practices: Organizations can learn from each other’s successes and challenges, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Collaborate on Solutions: Stakeholders can work together to address shared sustainability challenges, leveraging collective knowledge and resources.
A Catalyst for Actionable Change
SyncFrame goes beyond a mere reporting tool; it aims to drive actionable change by empowering organizations to identify and prioritize material ESG issues, set measurable goals, and track progress over time. The framework’s data-driven approach enables organizations to make informed decisions based on robust evidence, leading to more effective and impactful sustainability initiatives.